As you are new to the world of franchising, you might find it difficult to narrow down the franchise options. This is where a franchise consultant can help you.
TOP 15 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN A FRANCHISE AND GOING OUT ON YOUR OWN
By Tom Scarda, Certified Franchise Executive – Founder The Franchise Academy
To start a business, you have two options – a) Franchising or b) Starting a new business on your own.
Franchising refers to becoming a part of an established company by getting a license to use their company name, business model, marketing tools, etc., from the franchisor.
On the other hand, if you start a new business, you have to develop a product or service, business plans, marketing strategies, etc., by yourself.
There is a myth that franchising is more expensive than starting from scratch because of all the fees. However, in the long run, it may prove to be less expensive, especially if you fail.
Are you wondering – which one is the best? Are franchise consultants correct in saying – Franchising is better than starting a new business?
Read along; our list of top 15 differences between franchising and traditional business will answer all these and much more.
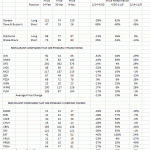
Sr. No Details Franchising Traditional Business
1 Business Idea In franchising, you leverage an already existing idea, no need to recreate the wheel. In a traditional business, you have to start from scratch and develop an idea by trial and error.
2 Workflow and processes Tried and tested workflows and operations are already established. You have to create all the processes and workflows on your own.
3 Support You will be given total assistance from the company/franchisor. There will be no external help in a traditional business until your business becomes successful.
4 Marketing In franchising, you will get better reach as the franchisor will provide you with effective marketing designs and collateral. You will know exactly who your customer is and where they live. You have to design several marketing campaigns and apply the most effective campaign. This will drain your bank account.
5 Required time With franchising, you can launch your business operations immediately in some cases. Initially, you will require at least 12 – 24 months or more to set up a business. You have to try and experiment with ideas and marketing campaigns while managing finances, logistics, and more.
6 Risk There is less risk in franchising because the business model is successfully running in multiple locations and you’re just plugging in. Traditional businesses come with higher risks as you are experimenting with new ideas that may or may not work upon launch.
7 Upgrades and development The company will provide you regular updates to scale your franchise. Moreover, the company will recommend new upgrades and innovations that have passed their R&D phase. You have to update your technology and workflows to suit the ever-changing consumer demand. No other company will push updates for your business.
8 Business plans, marketing guidance, training, etc. You will be guided by the company experts in all aspects of the business from marketing to recruitment, everything A to Z. In a traditional business model, you have to chalk out plans, discover new marketing campaigns while also training yourself. In simple words, you have to do everything by yourself.
9 Investment required As the business model is well-established, you get a clear picture of your initial and recurring expenses before you buy the franchise. Here, everything is based on trial and error; thus, you never get a clear estimate of your business expenses. As a result, you spend a much higher amount in setting up a new business.
10 Expert advice, feedback, and testimonials You will receive feedback, testimonials, and expert advice in a franchising model as there already exists a community of franchises. Getting expert opinions is a distant dream in a traditional business model. YouTube videos, blogs, and books will not help much as they are not directly related to your new business idea.
If you wish to get one-on-one advice from an expert, you have to pay out extra bucks.
11 Brand Identity Your franchisor has an established brand with recognized processes, trademarks, Intellectual property, and Google awareness. As a franchisee, you will enjoy all the benefits of an established brand. Starting a new business will take a few years to establish yourself as a brand with trademarks, confirmed processes, and IP and get on Google’s first page search.
12 Chances of success In franchising, you have proven business processes, marketing tools, and well-researched business upgrades. Also, if you face any challenges, you have a community of franchises to take help from.
All of these factors increase the chances of success by manifolds. You will face unforeseen challenges at every step of your business. Reinventing the business wheel with no external support makes it difficult to grow a business. Now you know why do 9 out of 10 startup businesses fail in the first couple of years.
13 Return on investment As you have a clear idea of expenses and a tried-and-tested business model in your hands, the return on investment for a franchisee is much higher. In a startup business, you will hardly make profits in the initial years. Also, if your business does well, you will have to re-invest a sum of your profits to further grow your business. As a result, your ROI remains negligible in the first few years of your business (and who knows whether the business will last long).
14 Customer base As a franchisee, you will benefit from the loyal customer base of the company. You don’t need to develop trust among customers; instead, you need to stand up to their loyalty to the company while developing trust among new customers. In a new business, you have to establish a customer base from scratch.
15 Easy access to finance Banks are more likely to approve loans as you are associated with a reputable franchise brand. New businesses come with high risks. As a result, banks will hesitate to bet on a startup business.
Which is better for you?
The Bottom Line – How to Choose a Franchise?
Now understand that franchising has several benefits over starting a new business, you must be wondering – How to choose a franchise?
To filter a franchise option, you should –
1. Research – Enquire about the policies, credibility of the franchise, work culture, terms and conditions, etc.
2. Weigh your pocket – Research the expenses and choose a franchise that suits your budget.
3. Read the FDD – Before finalizing a franchise, you must carefully read the Financial Disclosure Document (FDD).
As you are new to the world of franchising, you might find it difficult to narrow down the franchise options. This is where a franchise consultant can help you.
A reputed franchise consultant, one who has owned and operated franchises and has a CFE at the end of his or her name, will handhold you through the entire franchising process, from finding a franchise to setting up a franchise and beyond. Or the result is that you find out that franchising is not the right fit for you. If that is the case, at least you made that decision to not move forward based on facts and not myths and misnomers.
If you wish to avoid any missteps when starting your franchising journey, you can chat with me . It’s always free of charge! Book a time today: www.GetWithTom.com
ABOUT THE AUTHOR:
Tom is a Certified Franchise Expert. He was the #1 franchisee of the year in one franchise concept and failed in another. The lessons learned from failure is what makes him an expert. Tom is the author of several books including the #1 Bestseller, Franchise Savvy: 6 Strategies that Pros Use to Pick Top Performing Franchises. He has helped more than 1500 people figure out if franchising is for them since 2005.
#FranchiseOpportunities #controlyourdestiny #changeyourlifetoday