The business model is relatively simple. Once on the DoorDash platform, the company will take orders and deliver those orders for a fee ranging from 15-30%. At the same time, DoorDash charges the customer a service fee and a delivery fee that ranges from 15-25% of the cost of the order.
DOORDASH (DASH) – IN A HUGE STATE OF FLUX AS THE PANDEMIC WINDS DOWN
By Roger Lipton with permission

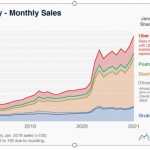
DoorDash is one of the largest “local logistics platform” i.e., food delivery firm, with 450,000 merchants, over 20 million consumers, 1 million Dashers (drivers) and 1.2 billion orders completed since the founding. The company has a 50% market share in the U.S. Revenue growth over the last five quarters has averaged over 211% with Q4 2020 revenue growth coming in at 226%. However, the company has lost over $1.2B since inception and lost $312M in Q4 2020. In preview of our summary: the fact the company cannot make money in the most ideal environment for its business model in 2020 is concerning. So is the fact the company has 46 pages of risk factors listed in its 10K.
We also point out that, while we are providing some “food for thought” below, third party delivery is a complex subject and in an enormous state of flux, so we don’t expect that we can answer every potential concern within these pages. We have stated before our reservations about the enormous capitalization of DASH ($42 billion as of today) and our concern about future operating margins for all the major third party delivery companies. Our intention here is to present what we can, in the hope that our work will be useful to the restaurant companies with which we have a working relationship.
THE BUSINESS MODEL
The business model is relatively simple. Once on the DoorDash platform, the company will take orders and deliver those orders for a fee ranging from 15-30%. At the same time, DoorDash charges the customer a service fee and a delivery fee that ranges from 15-25% of the cost of the order. The company pays the driver out of these fees and keeps the rest to operate its business.
DoorDash and the other food delivery companies such as GrubHub and Uber Eats, were primary beneficiaries of governmental policies that either closed or significantly restricted seating options for most restaurants. Adding a delivery service through DoorDash, GrubHub or Uber Eats was one of the few options available to restaurants and was therefore a requirement to stay open. Obviously when demand for your service is almost mandated by the government, you are going to grow your business tremendously.
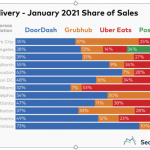
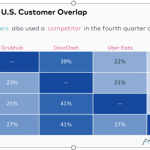
While DoorDash holds a 50% market share nationally, the company’s dominance is not universal across the country. In many of the major markets the company’s market share is less than 40%, which means that competition remains fierce, and this should keep margins under pressure in the long-term and advertising costs and competition for drivers increases. The lack of customer loyalty, as illustrated by the large overlap of usage of other deliver platforms, is also a long-term problem.
THE REVENUE BASE
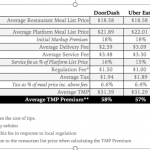
DoorDash makes money by charging both the restaurant and the customer. While the company does not report its actual fee structure, the practical result is that DoorDash is charging the merchant an average of about 18% of the cost of the order, though that fee is apparently negotiable from 15-30% of the cost of the order. In addition to charging the merchant, DoorDash also charges the customer fees ranging from 12-18% of the order. The average order size is approximately $37 and only 20% of orders are for more than $50. It remains unknown to what extent this is a long term sustainable model, when the profit margin of the restaurant is materially compromised and the customer ends up paying 40% or more above dining within the restaurant or picking up the food themselves. It is also not yet clear to what extent delivery cannibalizes dine-in or pick up sales.
It is important to note that cities are passing “Temporary” Price Control Regulations in response to high delivery fees.In response to companies such as DoorDash charging upwards of 30% of the cost of an order in fees. cities are starting to pass regulations to cap the fees third-party ordering services can charge restaurants. For example, in the company’s Q4 2020 investor letter, DoorDash co-founders, Tony XU and Prabir Adarkar, stated that there are now 73 jurisdictions imposing temporary price controls, which is more than double the 32 jurisdictions in the third quarter. Generally speaking, these price controls cap the amount of delivery fees charged the merchant to 15%. The controls have predictably negatively impacted DoorDash’s profitability.
The company disclosed that the net impact of price controls in Q4 2020 was $36M or 44bps of profitability. The company expects the impact of price controls to almost double in Q1 2021. In the meantime, DoorDash is trying other measures to manage these caps. The company is charging an additional $1 to $2 fee in at least 11 municipalities that have caps in place. In Denver and Chicago, DoorDash began charging customers a $2 “Denver fee” and $1.50 “Chicago fee” per order. While these price controls are said to be temporary, that remains to be seen.
THE ECONOMICS FOR RESTAURANTS, CONSUMERS, & DRIVERS (“DASHERS”)
The Restaurants
The pre-tax profit margin of a restaurant generally ranges from 5-10% of revenue at the corporate level. If a restaurant is having to pay DoorDash 15-30% of an order, and DoorDash does a material portion of the sales, the company’s profit margins can easily drop by a couple of hundred basis points. If deliveries become 30-50% of total revenue the company could turn unprofitable. While some of the deliveries may currently be incremental business, and a year ago publicly held companies were accepting that premise, we haven’t heard anyone making that claim recently. While we have no doubt that delivery sales in aggregate will be higher going forward, it is questionable whether the current growth is sustainable because of the high cost to both consumers and restaurants.
In addition, by utilizing drivers from third parties, the restaurant loses the direct relationship with the customer and there is no incentive for the driver to enhance the customer experience with any particular restaurant. This lack of control and incentive could negatively impact the customer’s relationship with the restaurant. Drivers for pizza chains like Domino’s and Papa Johns are more incentivized to enhance the customer experience because they can move up the ladder at these firms and many have eventually become franchisees. There is no upward mobility for drivers at DoorDash.
Every major restaurant chain has its own app that it uses to take orders and communicate with its customers. More importantly, when a customer uses the restaurant’s app, they gain valuable information, such as order size, composition and frequency, that the company can use to improve customer relationships. They can also offer loyalty rewards and other customer-centric offers, such as sales on specific food items.
On the latest Brinker International earnings call, CEO Wyman Roberts said that DoorDash only offers high level information about orders for their Just Wings virtual brand offered on DoorDash. Because they do not share individual customer data, it complicates their marketing and data collection efforts. In the long run, we think most major brands will try to increase customer usage on their proprietary apps and reduce reliance on third-party delivery services for customer acquisition.
As more people go back to work, we believe the necessity of paying huge markups for food delivery will diminish and DoorDash will lose a big tailwind. We also believe that companies like Brinker or Darden that already have large To-Go offerings will try to replace delivery with more To-Go orders. It is a win-win for the company and customers. Customers pay significantly less, even including drive time to pick up their food and the company saves the fee they pay DoorDash. The restaurant leverages their existing infrastructure and gains more valuable data on their customer that can be used to increase sales and profitability. It can also improve kitchen efficiency.
The Consumers
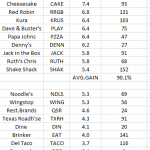
To recover some of the fees, many restaurants are increasing the menu prices for items ordered for delivery. Researchers in Minneapolis recently conducted a case study of delivery platforms to compare pricing and consumer fees.
There are several takeaways from this case study.
Since restaurants appear to be marking up the menu price to recoup most of the DoorDash fee, the customer is paying 40-60% more than they would by eating in the restaurant and this is before the tip. It is therefore clear that DoorDash is the largest beneficiary, in this simplistic example, without considering the customer acquisition cost or the sustainability of the model in terms of satisfying the drivers and food consumers.
The Restaurant Business editorial staff did a test ordering chicken sandwiches from various fast-food concepts. It reported that some editors paid $15 or more for a single sandwich to be delivered. As one editor stated,
“My cost to have Chick-fil-A delivered to my home was roughly the same cost as I paid to east out at a local Mexican restaurant.”
The “Dashers” – a few problems
Similar to Uber and Lyft, the DoorDash business model relies on independent contractors utilizing their own vehicles to provide the service to customers. According to the 10K, there were 1 million Dashers (drivers) and their total earnings were $2B. Though Doordash says on their website that a Dasher can make between $15-$25 an hour, dividing $2B by 1M drivers amounts to $2,000 per year, $167/month, or $40/wk. Since over 90% of Dashers work less than 10 hours a week, this would amount to only about $4.00/hr. The company touts examples in California where Dashers earn $33-$36 an hour working less than 7 hours a week ($1000 a month) in various cities. We believe these figures are clearly outliers and not representative of the true earnings potential of a Dasher. Moreover, relying on a worker that only wants to work 10 hours a week for less than $167 a month does not seem to us to be a way to maintain a consistent, quality experience for the customer.
There is also a growing political pressure to increase the pay and benefits to so-called “gig workers”. A group in Washington state called Working Washington is running a “Pay Up” campaign to increase the income of these workers. The group published a study on the net income of Dashers in Washington state. We encourage subscribers to read it. The conclusion was startling, supporting our calculation above:
“On average, DoorDash pays just $1.45 per hour worked, after accounting for the expenses of mileage and the additional payroll taxes borne by independent contractors. The average job requires 6.8 miles of driving and takes 30 minutes to complete. “
As a result of negative publicity and new legislation, the company has already been forced to increase the amount it pays Dasher on a per order basis. The passage of Proposition 22 in California and the potential for other states to do enact similar legislation could cause the company to raise wages again. As discussed in the 10K, the impact of Proposition 22 on the company were as follows:
Amongst the 46 pages of risks in the 10-K are a few nuggets as they relate to these costs.
Several other states where we operate may be considering adopting legislation similar to Proposition 22, which we would expect to increase our costs related to Dashers in such jurisdictions. This could result in lower order volumes if we charge higher fees and commissions and could also adversely impact our results of operations.
Several jurisdictions where we operate may be considering adopting legislation that would pair worker flexibility and independence with new protections and benefits. To the extent these are adopted, we would expect the costs related to Dashers in such jurisdictions to increase and we could experience lower order volumes if we charge higher fees and commissions.
The necessity for DoorDash to improve the economic proposition for their Dashers will most likely reduce DoorDash operating margins because the merchants and consumers are already more than adequately burdened.
NOW – THE RUBBER MEETS THE ROAD – AND OUR CONCLUSION
Before presenting our conclusion, the following post by an industry insider on an investment website supports our concerns.:
As the pandemic winds down, it should be no surprise that recent guidance shows sharp deceleration in revenue growth for 2021.In the Q4 2020 earnings release and shareholder letter, the company issued guidance for 2021. While the company guided for 187% growth in revenue in Q1, revenue growth for all of 2021 is only expected to be 28%. This is a significant deceleration from the 200%+ growth in 2020. Wall Street is expecting revenue growth in 2022 to slow ever further to 26%. In addition, because of the increasing costs and limits on fee and commissions discussed above, the company guided adjusted EBTIDA to $0-$200M, considerably below the $250M Wall Street was expecting going into 2021. Underlying the slower growth, we think it likely that as more people go back to work, we believe the necessity of paying huge markups for food delivery will diminish. We also believe that companies like Brinker or Darden that already have large To-Go offerings will try to replace delivery with more To-Go orders. It would be a win-win for the company and customers, as customers pay less, even including drive time to pick up their food and the merchant saves the DoorDash fee. The restaurant also gains the valuable customer data that can be used to increase sales and profitability.
We believe the DoorDash business model is far from sustainable in its present form. It is especially concerning that DASH has reported nothing but red ink in an environment so enormously supportive of third party delivery agents. Though the stock is 50% off its highs, we do not think the Enterprise Value, still over $40 billion, is justifiable. The EV multiple is over 10x 2021 projected sales and an indeterminate multiple of the ridiculously large guided range of Adjusted EBITDA from zero to $200M. We are not long or short the stock, just saying 😊
About Roger Lipton
====================
Roger is an investment professional with over 4 decades of experience specializing in chain restaurants and retailers, as well as macro-economic and monetary developments. After earning a BSME from R.P.I. and MBA from Harvard, and working as an auditor with Price, Waterhouse, he began following the restaurant industry as well as the gold mining industry. While he originally followed companies such as Church’s Fried Chicken, Morrison’s Cafeterias and others, over the years he invested in companies such as Panera Bread and shorted companies such as Boston Chicken (as described in Chain Leader Magazine to the left) .
He also invested in gold mining stocks and studied the work of Harry Browne, the world famous author and economist, who predicted the 2000% move in the price of gold in the 1970s. In this regard, Roger has republished the world famous first book of Harry Browne, and offers it free with each subscription to this website.